Content Security Policy on Netlify (guide)
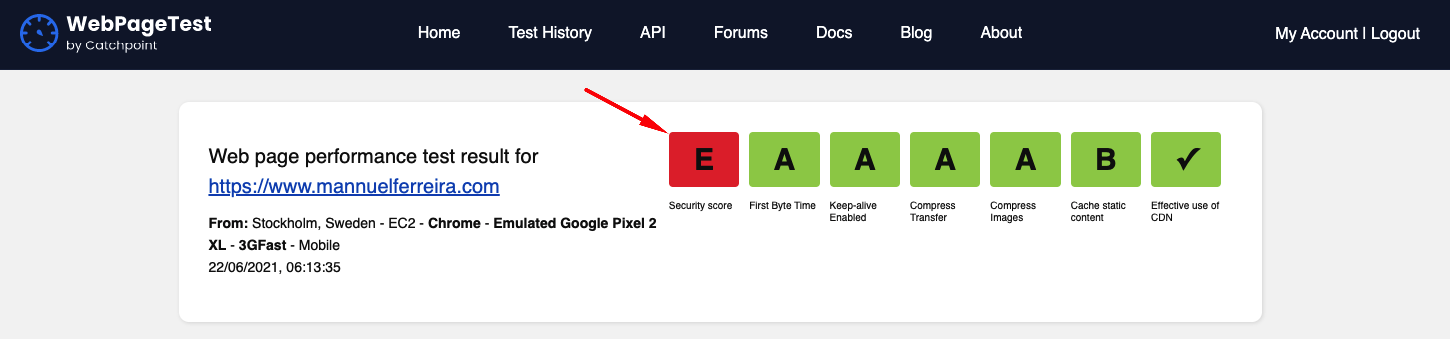
After deploying your website to Netlify naturally you run some performance tests using WebPageSpeedTest. You might notice and alarming red "F" or "E" in the top right of the screen.
After deploy your website to Netlify (or any server) naturally you will run performance tests using WebPageSpeedTest. You might notice an alarming red F or E in the top right of screen.
TL;DR
This is a security score linked to a CSP (Content-Security-Policy), it shows whether any security policies are configured. The CSP provides a way to control the loading and execution of scripts and media in your webpage.
Setting the correct directives will prevent clickjacking, code-injection, cross-site scripting, illegal embedding of your webpage in an offsite frame/iframe and allow only valid MIME types.
In my case, deploying to Netlify...
Created a netlify.toml file and placed the CSP policy like this:
[[headers]]
for = "/*"
[headers.values]
X-Frame-Options = "SAMEORIGIN"
X-XSS-Protection = "0"
X-Content-Type-Options = "nosniff"
Content-Security-Policy = "default-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; form-action 'self'; script-src 'self'; connect-src 'self'; img-src 'self'; base-uri 'self';"
That is a basic starter policy it allows css, form actions, ajax requests, scripts and images from the same origin, does not allow object, frame, media.
This is bare bones setup and no Google Analytics scripts or font scripts will be allowed to execute, keep reading to for more or checkout my final netlify.toml file.
The long story
Clicking on the red E icon will load the Snyk test results, which looks like this:

The Snyk test results page:
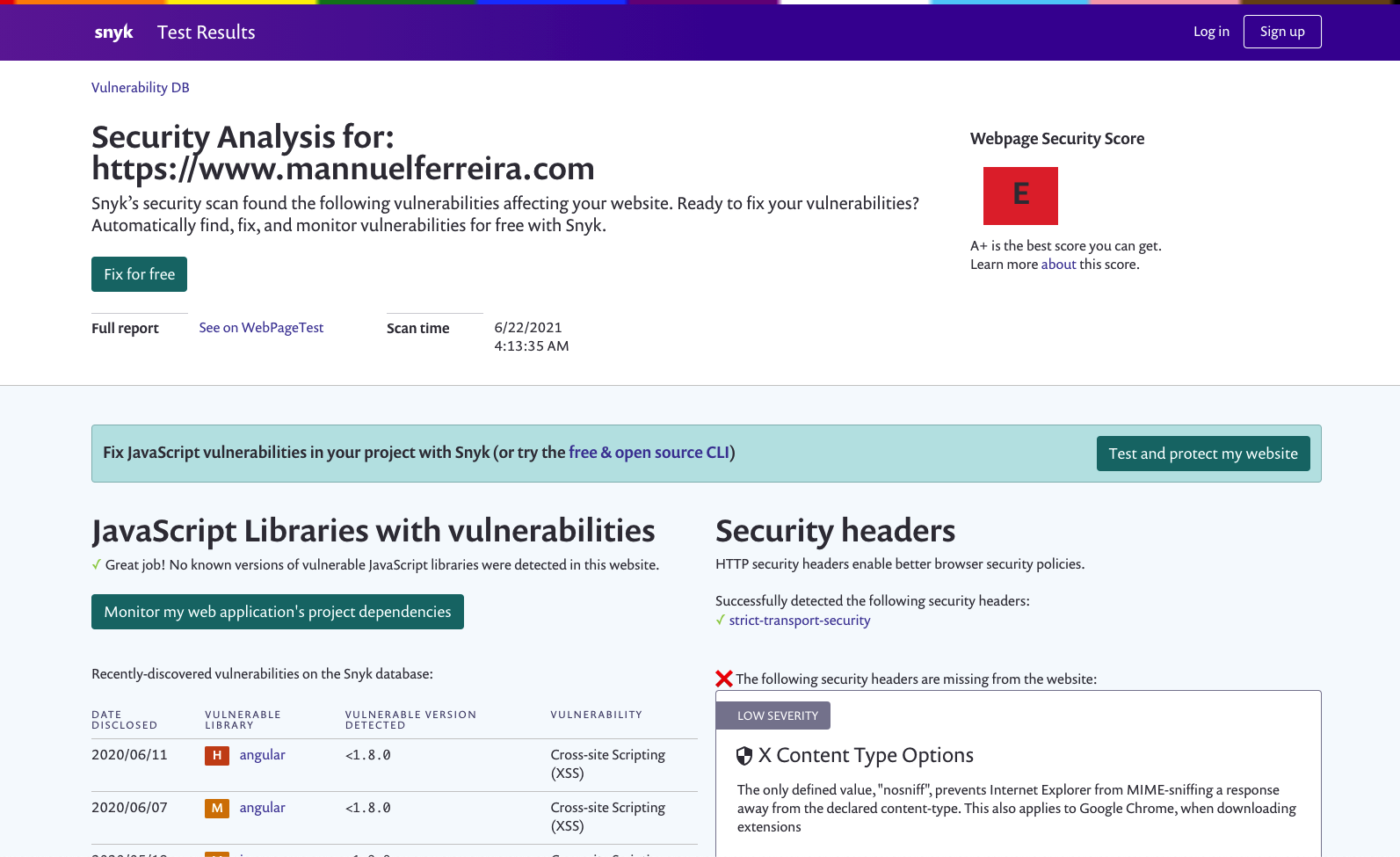
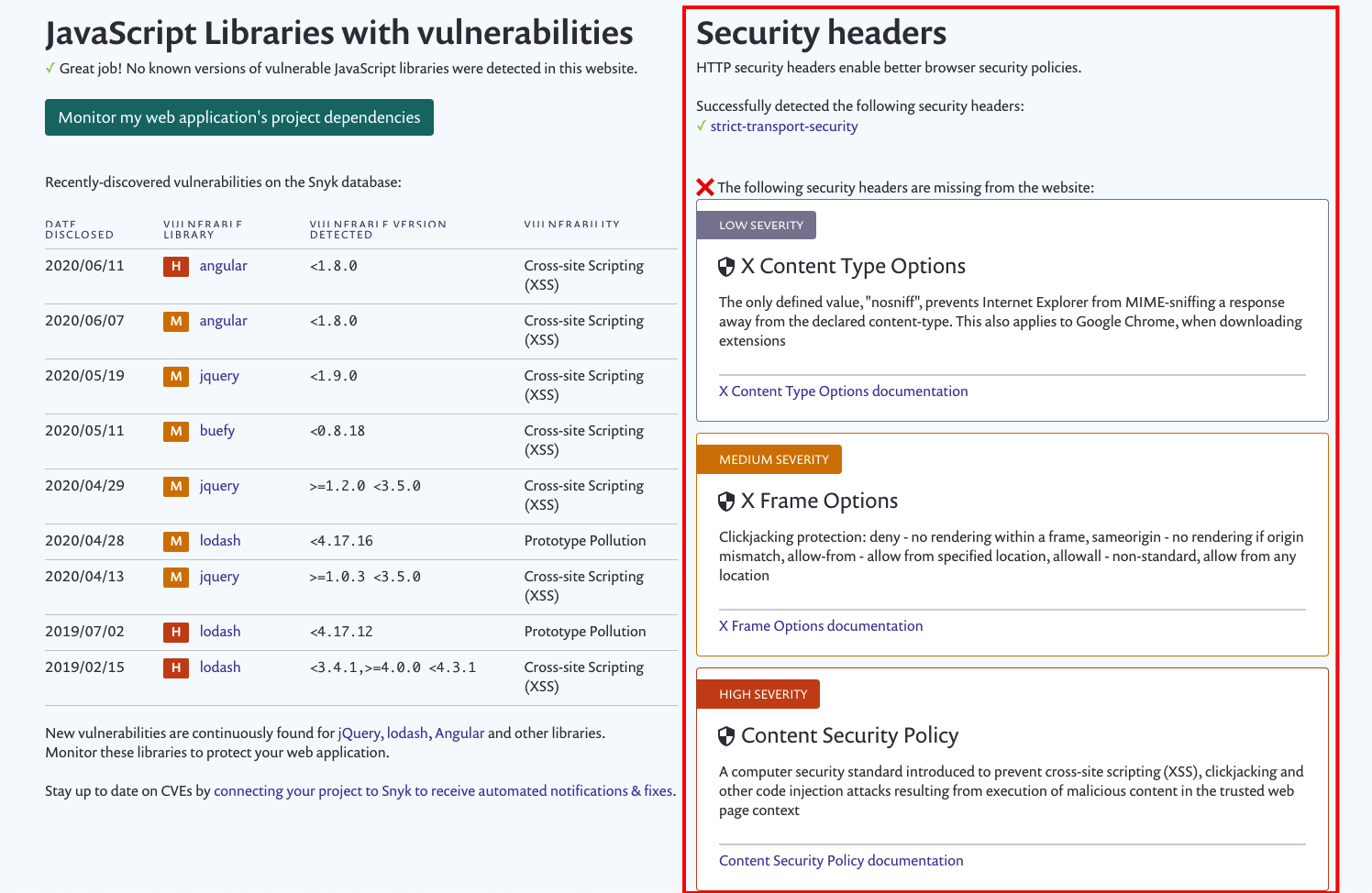
JavaScript Libraries with vulnerabilities
On the left you can see all the newest reported vulnerabilities in popular npm packages.
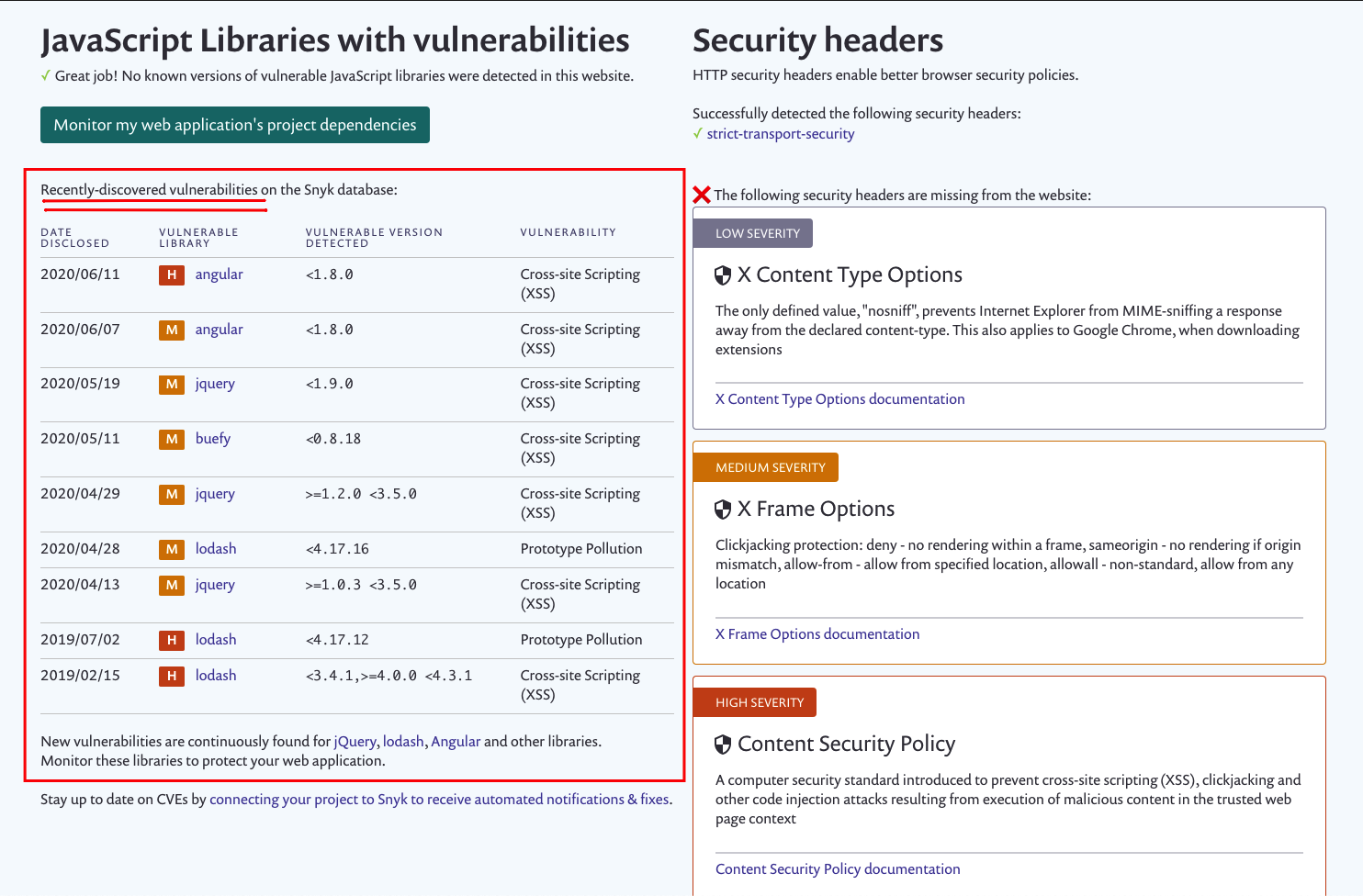
Security headers
On the right you can see our very own reported Security Headers related vulnerabilities.
netlify.toml
Okay back to the Headers, given these headers:
[[headers]]
for = "/*"
[headers.values]
X-Frame-Options = "SAMEORIGIN"
X-XSS-Protection = "0"
X-Content-Type-Options = "nosniff"
Content-Security-Policy = "default-src 'none'; style-src 'self'; form-action 'self'; script-src 'self'; connect-src 'self'; img-src 'self'; base-uri 'self';"
Once the Policy has been set above with the above configuration, upload and test it by opening the browser dev tools. Looking at the console, you will notice some errors that you have never seen before because you had no CSP configured.
In my case on Netlify deploy preview-mode I saw:
60d2b0fc45694e0008dd4d32--mannuelferreira.netlify.app/:1 Refused to load the script 'https://d33wubrfki0l68.cloudfront.net/bundles/1bd814911a09d5e56b421403a658cbae5d2685ce.js' because it violates the following Content Security Policy directive: "script-src 'self'". Note that 'script-src-elem' was not explicitly set, so 'script-src' is used as a fallback.
My CSP is preventing cloudfront.net above from executing in my webpage.
GREAT 🚀 looks like stuff is working.
Now I can decide to allow cloudfront.net because I trust Netlify and it's domains, so I should whitelist it by adding the domain and sub-domains to the default-src directive e.g.
Content-Security-Policy = "default-src 'self' cloudfront.net *.cloudfront.net; frame-ancestors 'self'; form-action 'self'"
Bare in mind this list has the potential to get lengthy the more scripts you plan to allow execution, you can see my: netlify.toml file.
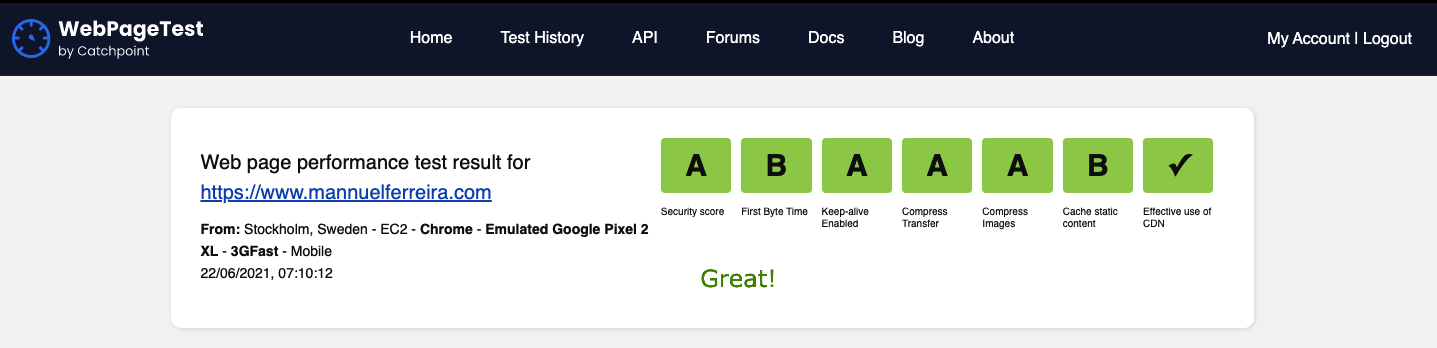
Rerun the test
WebpageSpeedTest results:
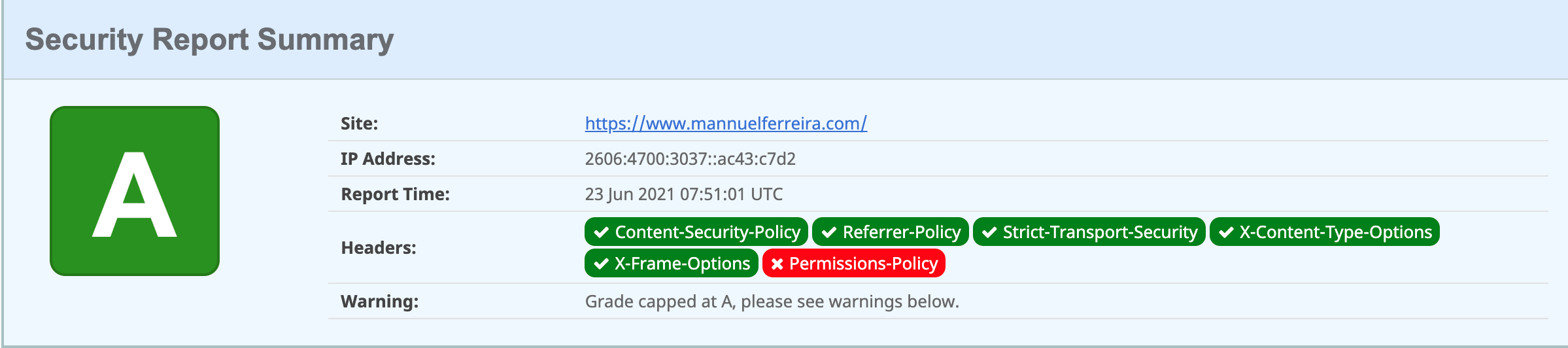
Security Headers results:
Not using Netlify? try one of these:
Nginx
server block.
server {
...
add_header "X-Frame-Options" "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header "X-XSS-Protection" "0";
add_header "X-Content-Type-Options" "nosniff";
add_header "Content-Security-Policy" "default-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; form-action 'self'";
...
}
Apache
.htaccess
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
Header set X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN"
Header set X-XSS-Protection "0"
Header set X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"
Header set Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; form-action 'self'"
</IfModule>
IIS
web.config
<system.webServer>
<httpProtocol>
<customHeaders>
<add name="X-Frame-Options" value="SAMEORIGIN" />
<add name="X-XSS-Protection" value="0" />
<add name="X-Content-Type-Options" value="nosniff" />
<add name="Content-Security-Policy" value="default-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; form-action 'self'" />
</customHeaders>
</httpProtocol>
</system.webServer>
CSP - Content Security Policy
CSP stands for Content Security Policy
DO NOT use X-Content-Security-Policy or X-WebKit-CSP. Their implementations are obsolete (since Firefox 23, Chrome 25), limited, inconsistent, and incredibly buggy. Read more here
Let's break it down
By adding those configurations to your server you are essentially creating a security policy.
A policy that tells the browser what to do with a request, allow it or block it based on what you've configured. Note the absence of this configuration will render your server in-secure.
(in order or appearance):
-
X-Frame-Optionsprevents click jacking by not allowing your webpage to be loaded in a frame or iframe. The SAMEORIGIN property allows a page to be loaded in a frame on the same origin as the page itself only.DEPRECATEDRead more- use Content-Security-Policy: frame-ancestors 'self'; instead
-
X-XSS-Protectionblocks any request that is deemed to be Cross Site Scripting Attack.DEPRECATEDRead more- use Content-Security-Policy: frame-ancestors 'self'; instead
-
X-Content-Type-Optionsprotects against MIME type confusion attacks, ensures to load a resource only if the correct MIME type of is a matched against what is expected. -
Content-Security-Policyallows you to set a custom policy on what scripts, urls, images, fonts and resources are allowed to execute in your webpage. Any resource that is not whitelisted will not be allowed to execute.